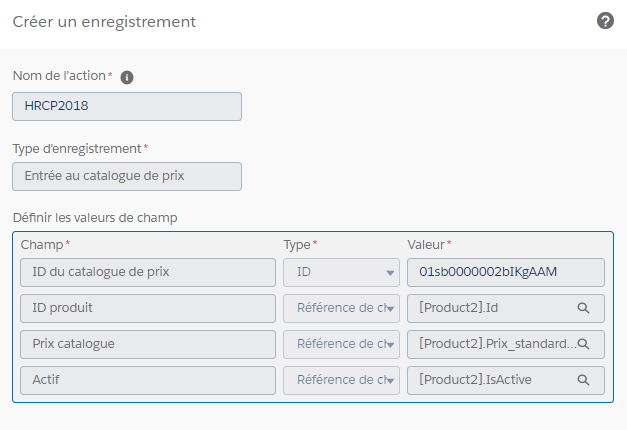
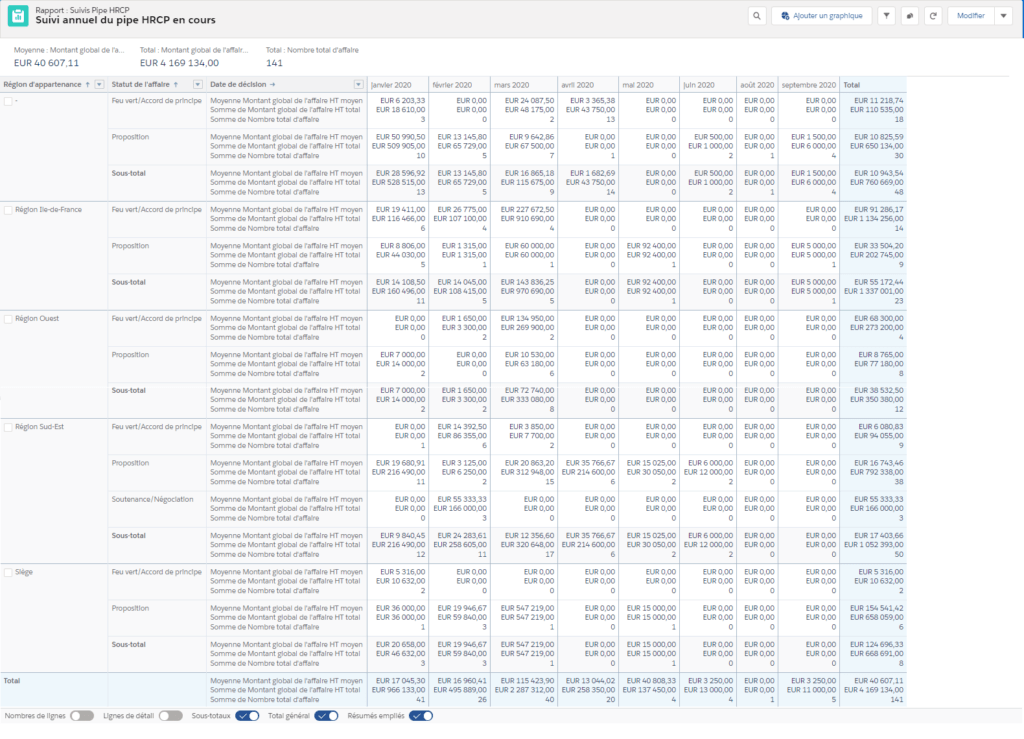
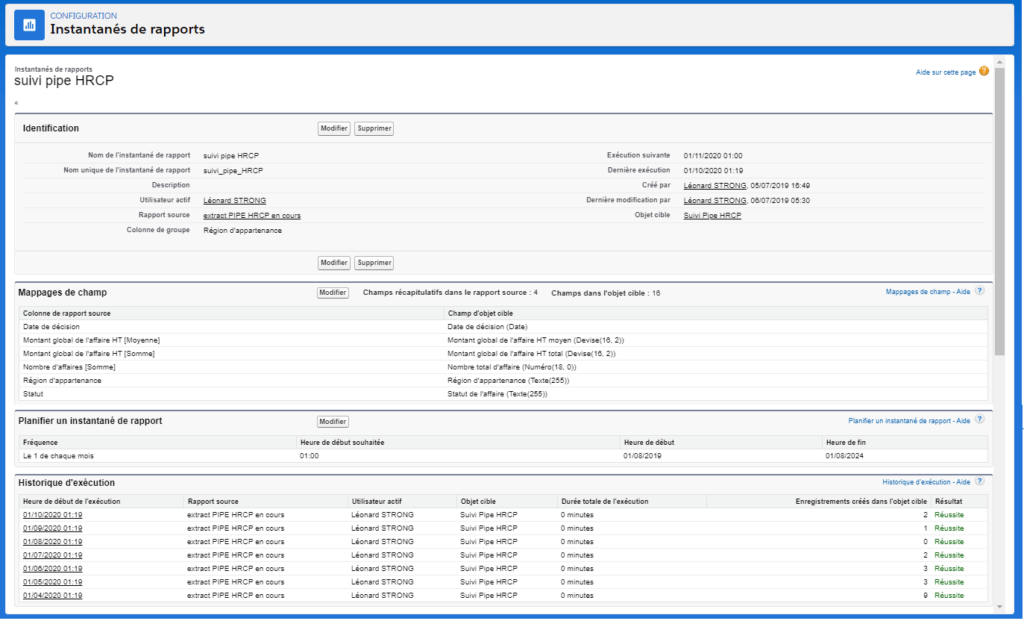
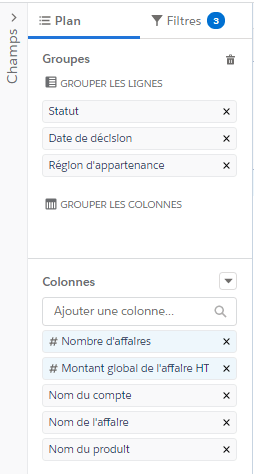
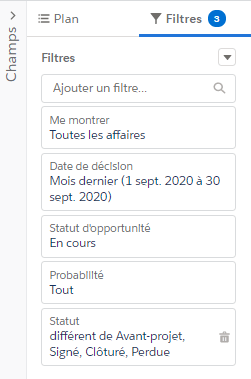
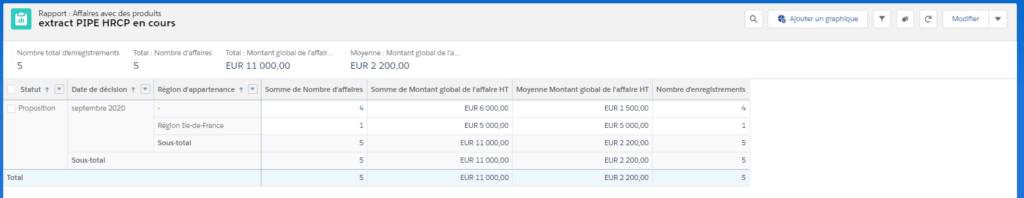
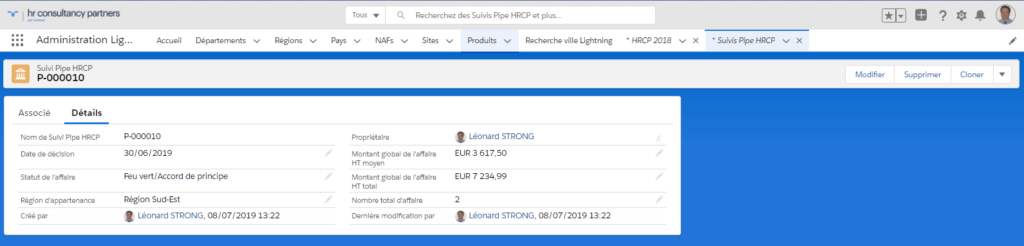
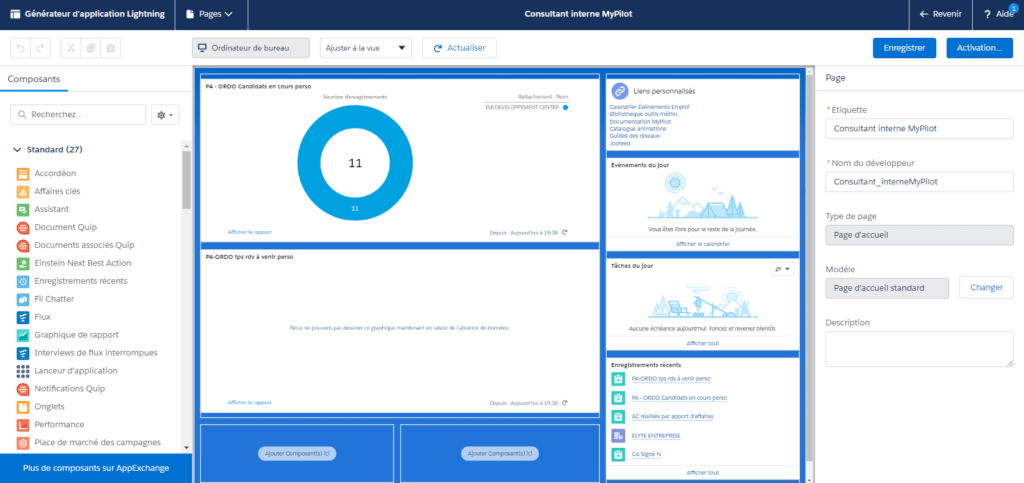
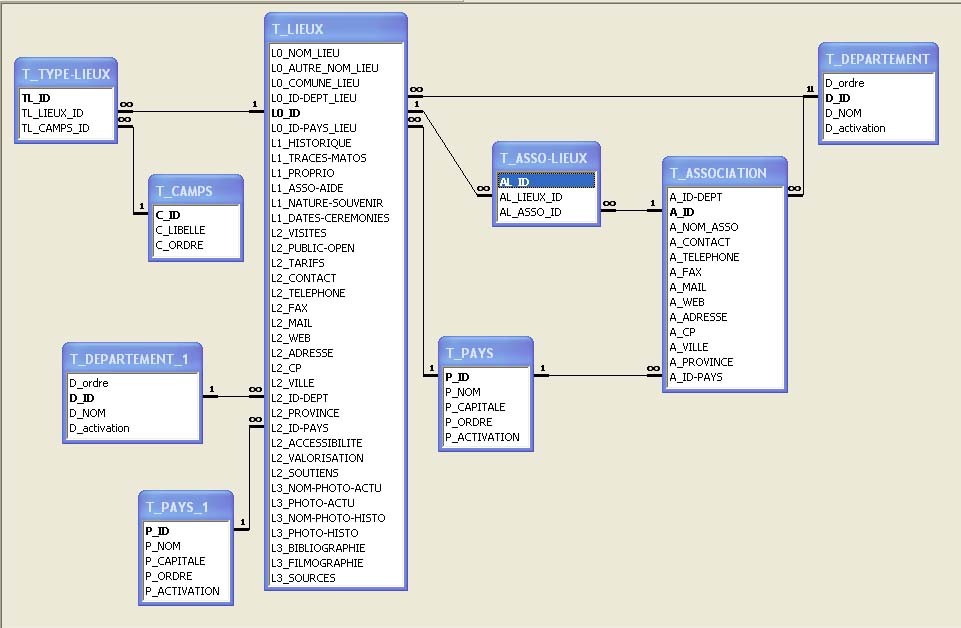
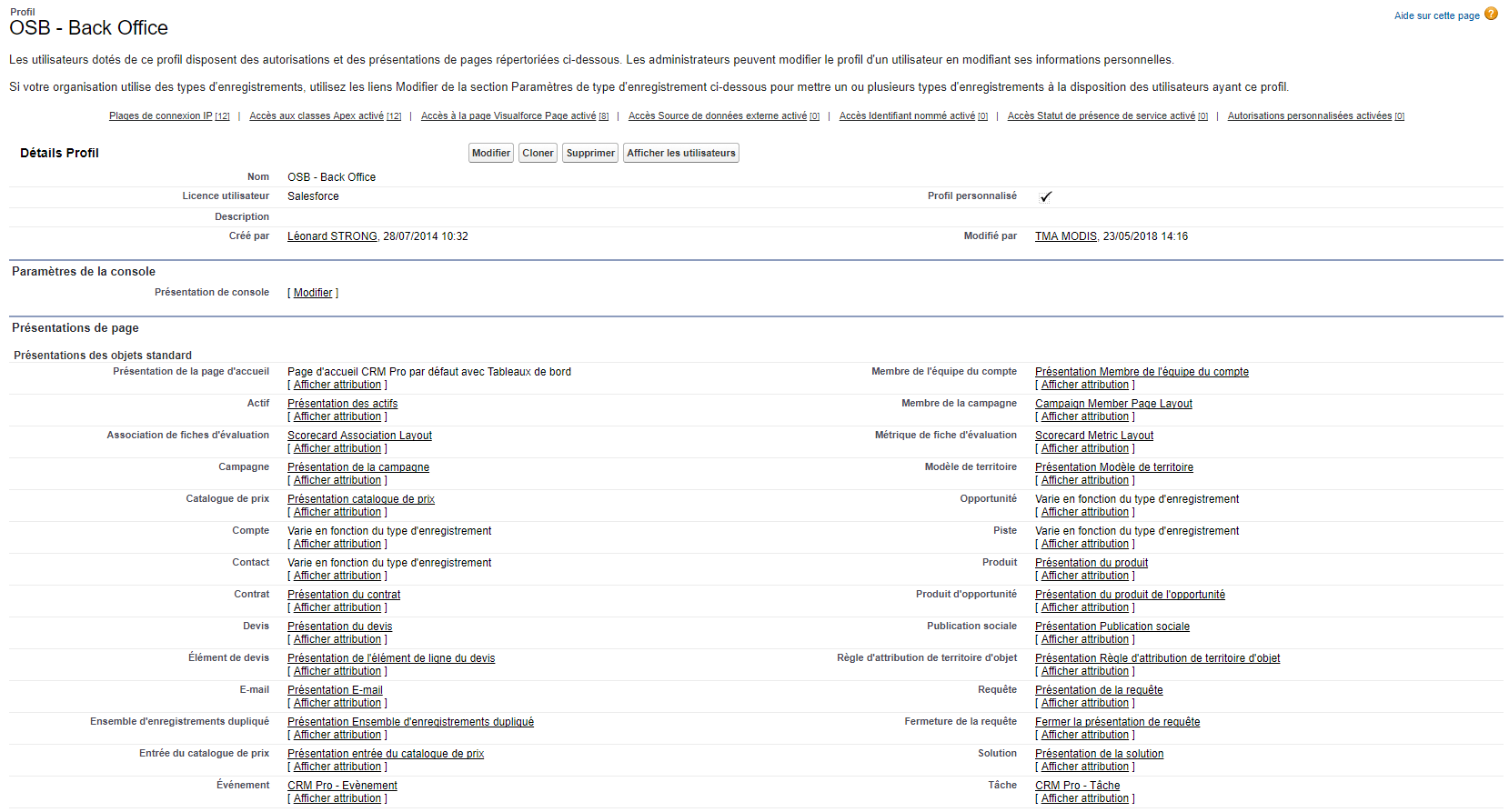
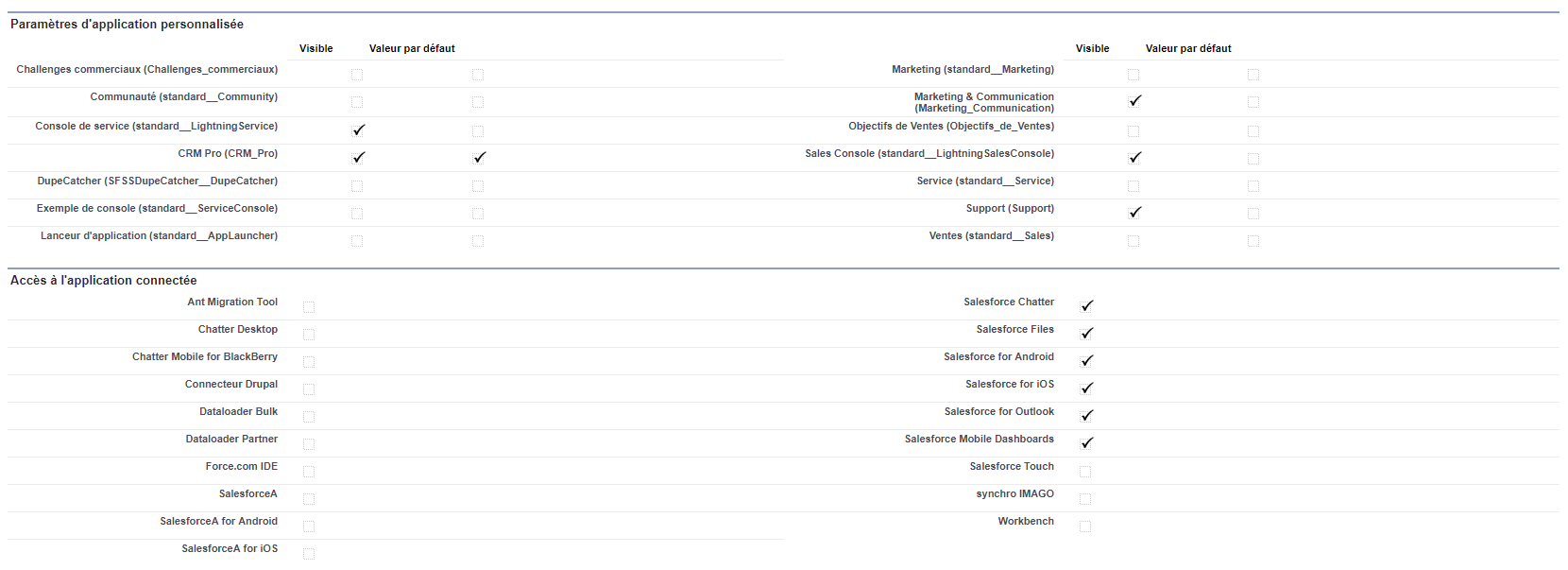
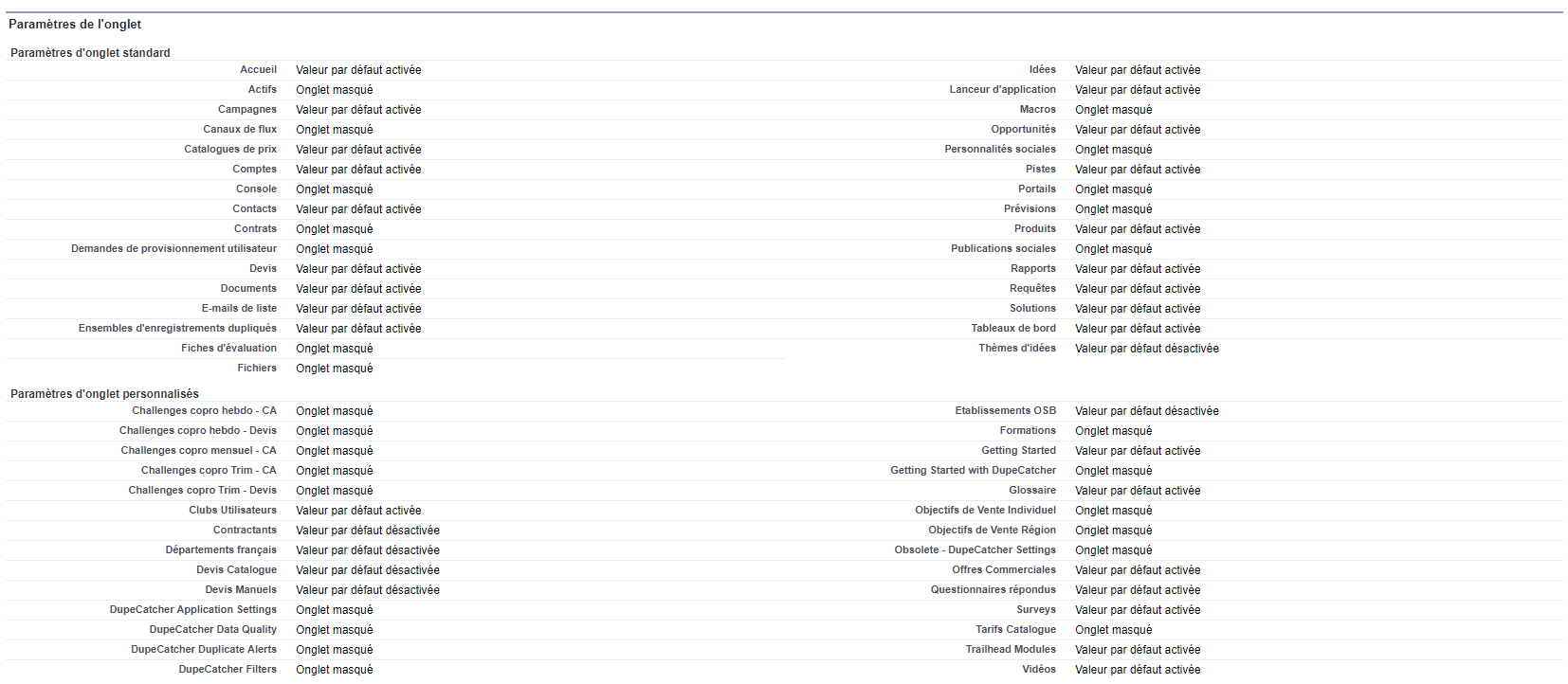
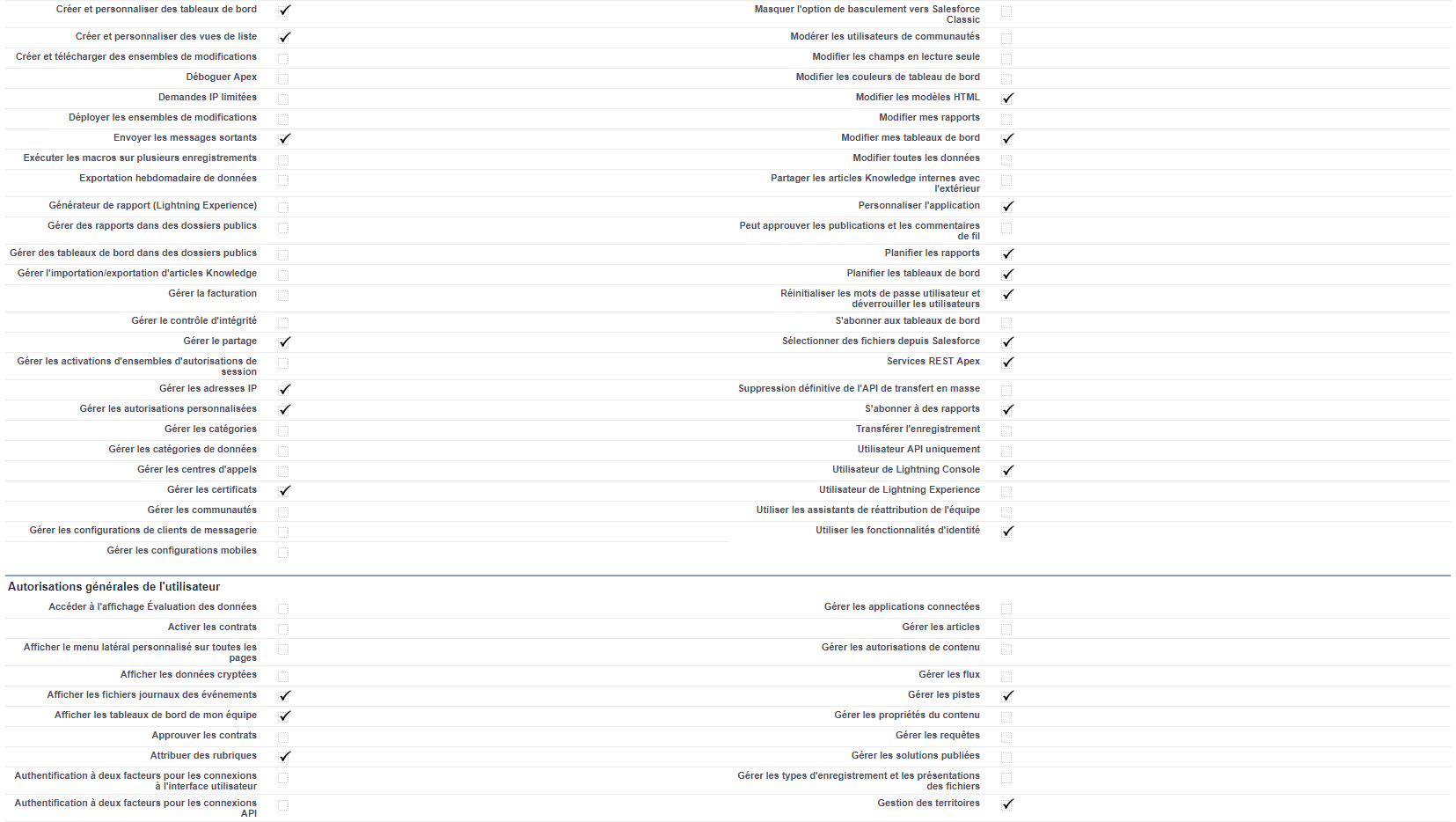
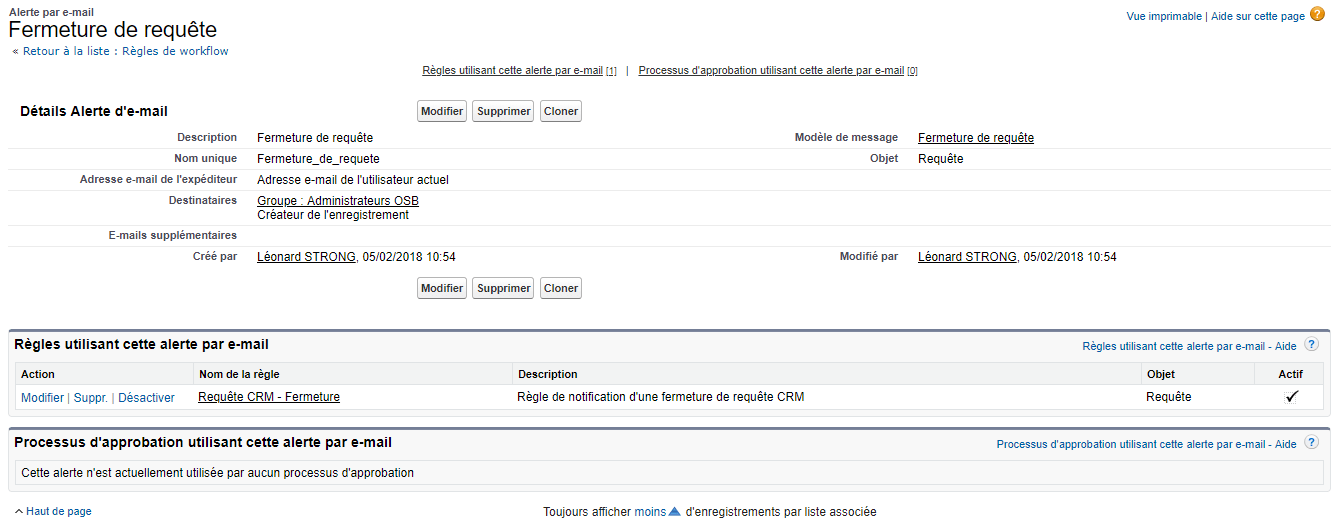
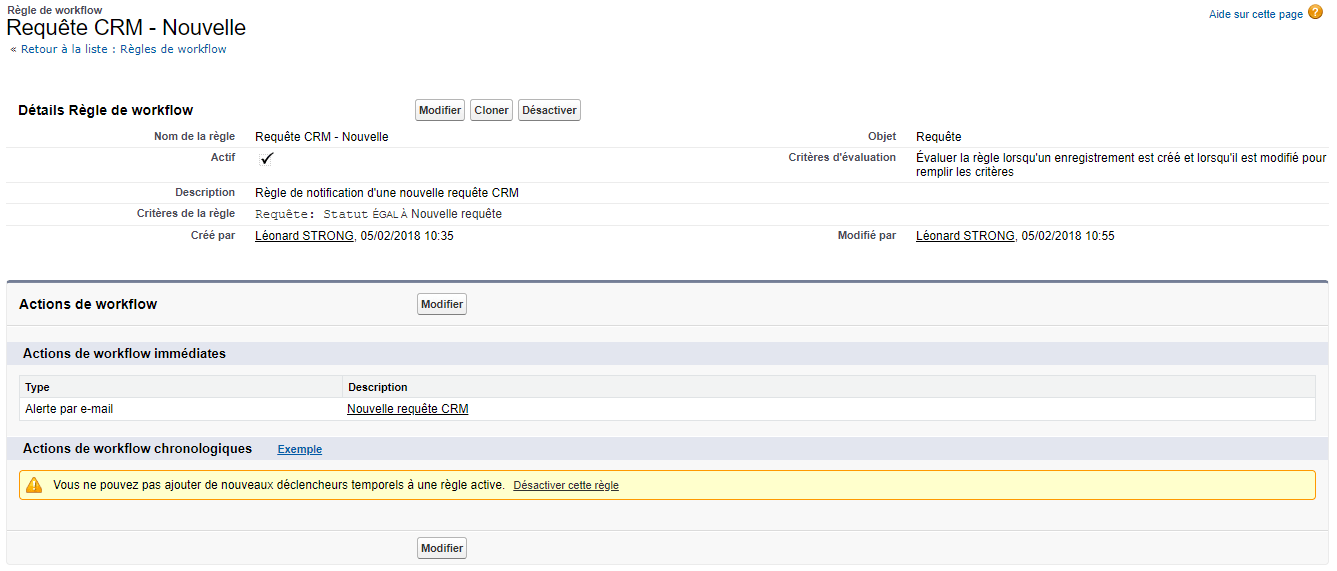
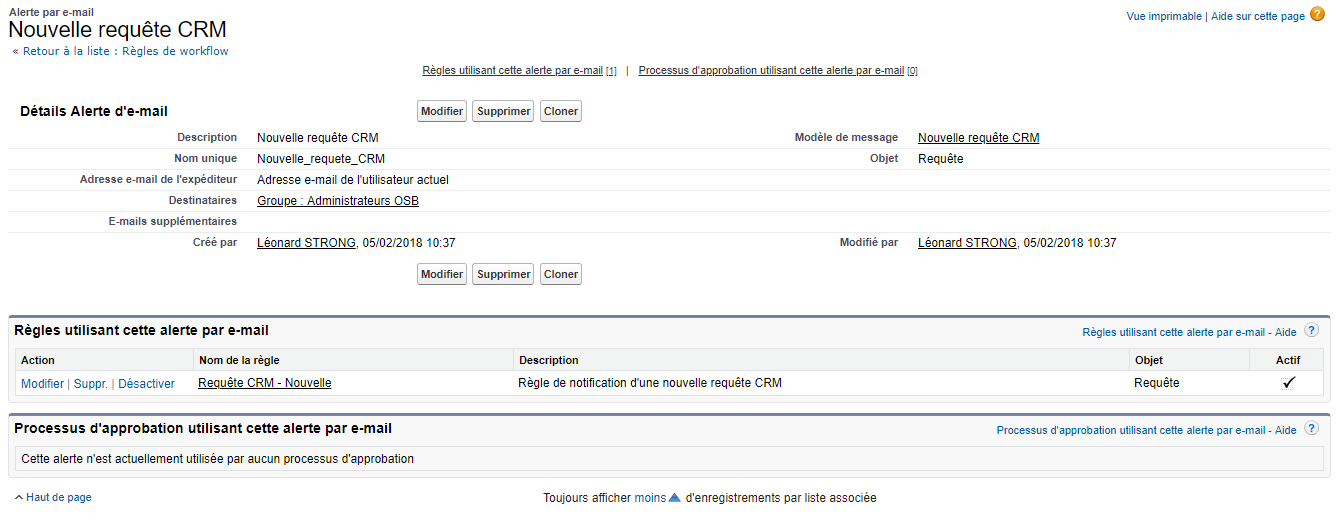
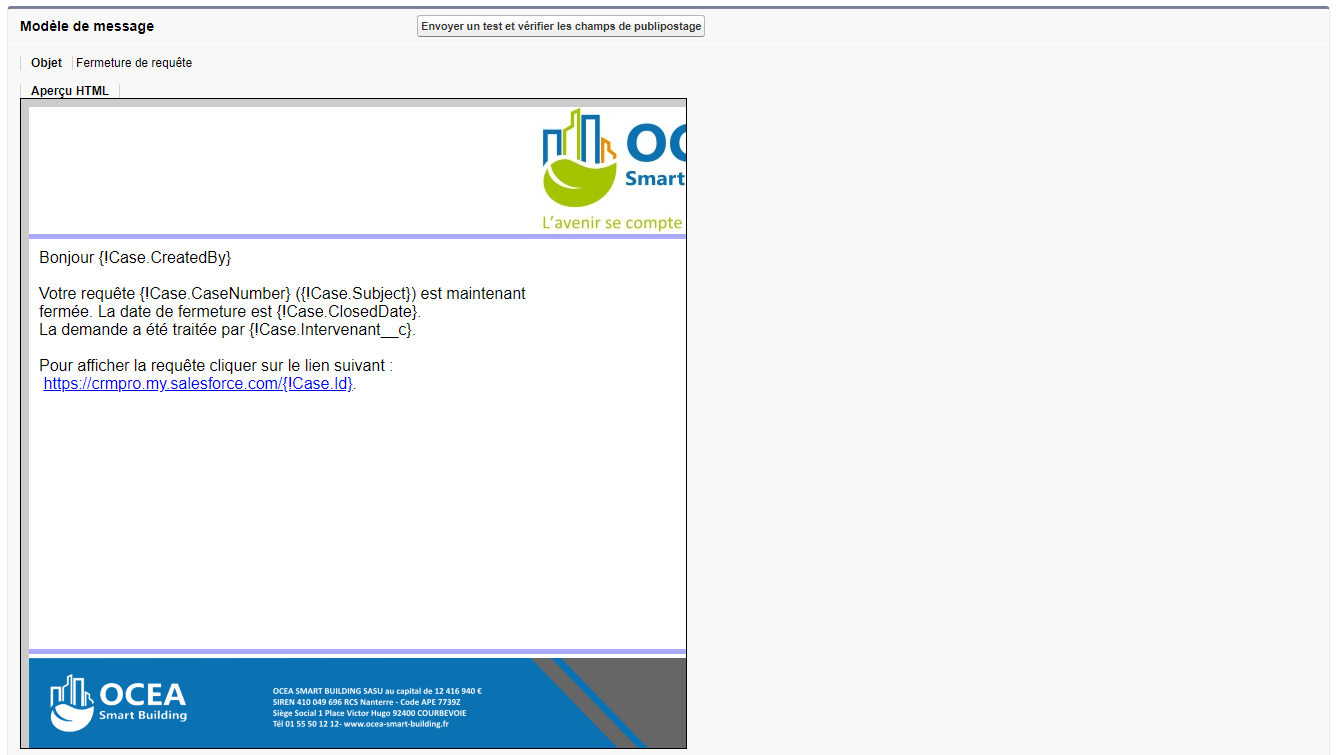
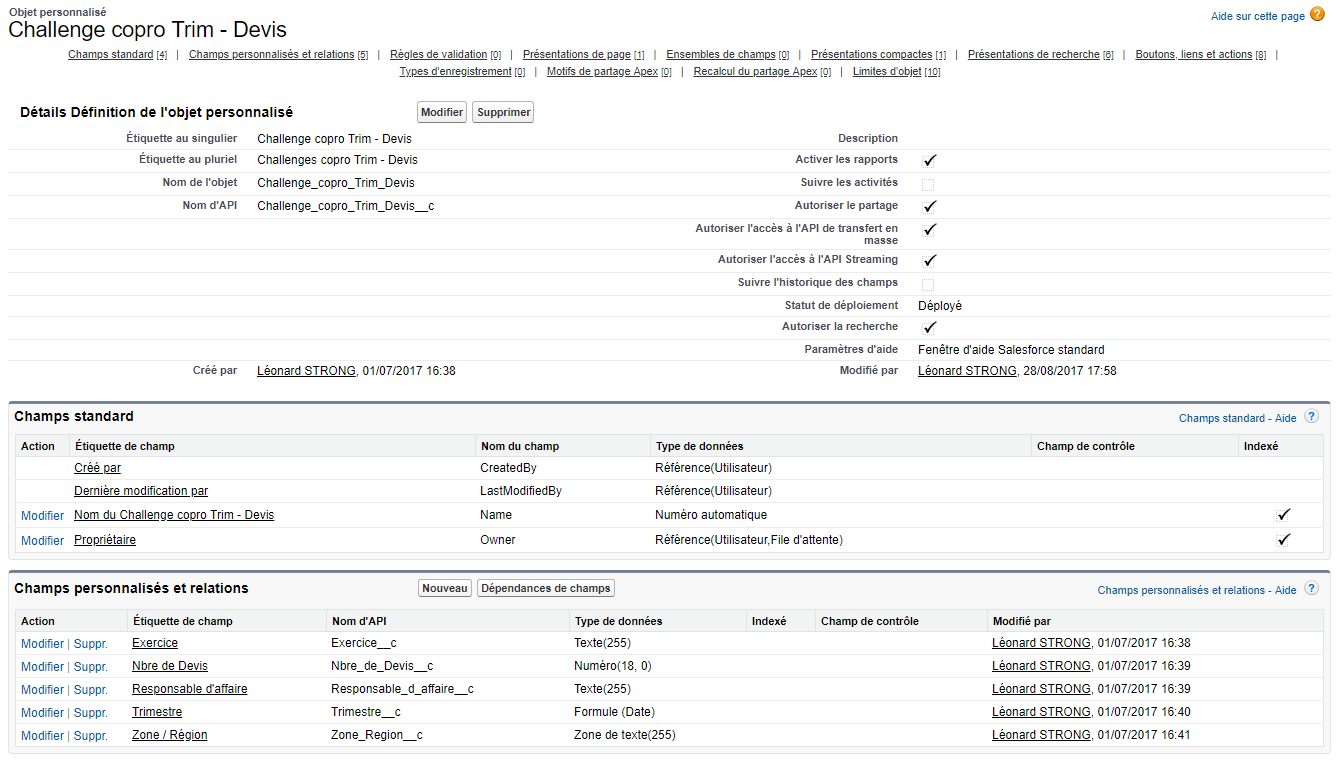
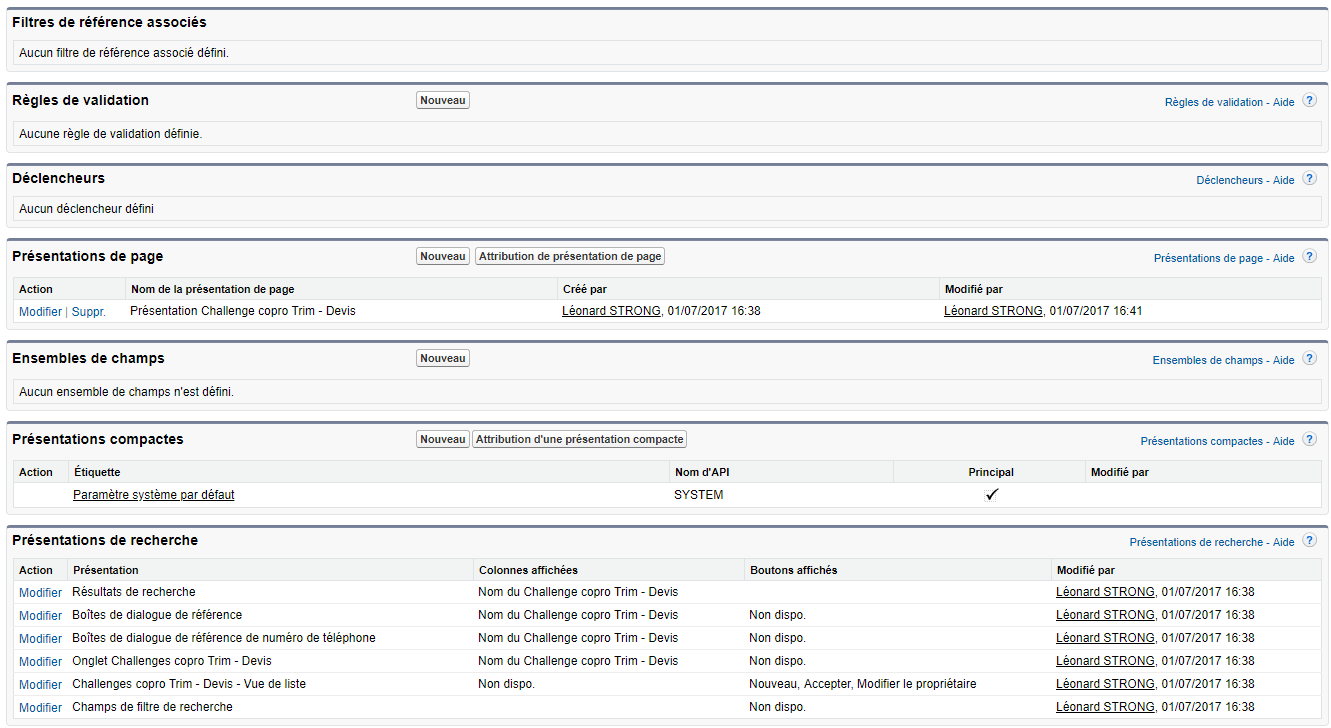
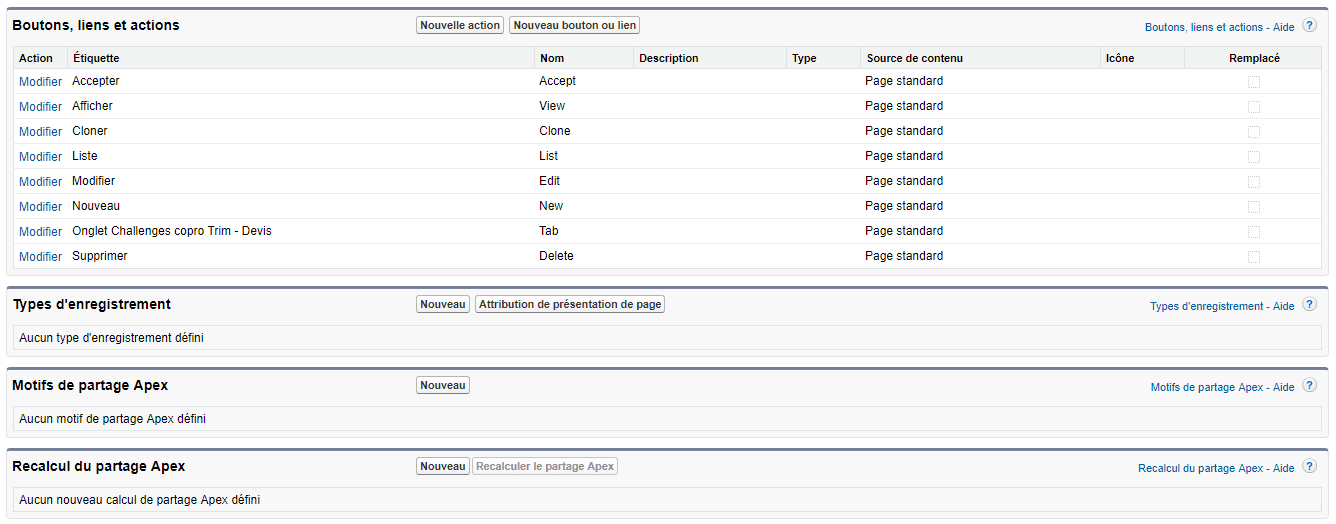
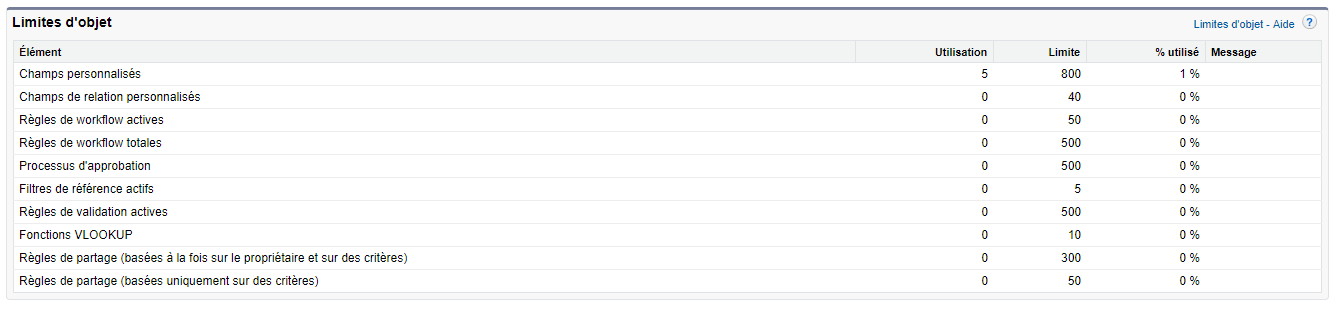
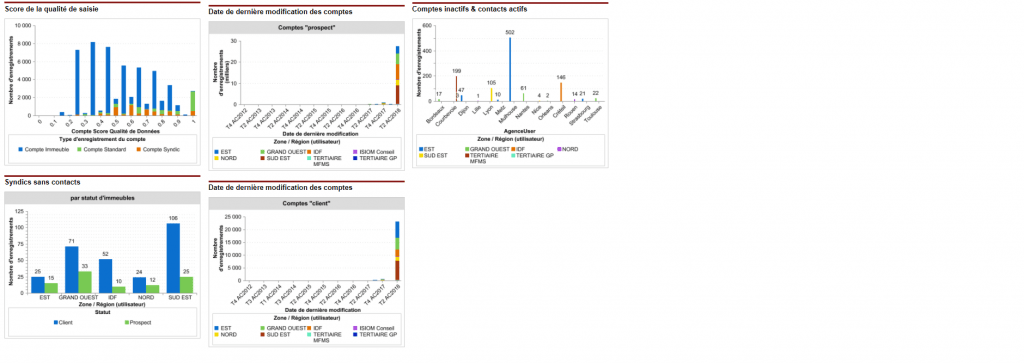
AM: Asset Management. Asset Management is a profession in finance which consists of managing the capital entrusted to it in compliance with regulatory and contractual constraints by applying internally defined investment policies, in order to obtain the best possible return according to the chosen risk.
The real estate asset manager optimises and enhances the value of real estate investments belonging to a natural or legal person. He/she ensures the commercial, administrative and financial monitoring of the real estate portfolio for which he/she is responsible.
Backlog: Product Backlog Scrum. Collection of customer requirements that the project team must achieve in the context of a Scrum project. It contains the list of features that make up the expected product. The constitution of the Scrum backlog begins with the materialization and definition of the product's objectives, the targeted users and the different actors of the project. The list of features is evolving. Items can be added, deleted or modified at any time.
CFA: Centre de Formation par l'Alternance. Organisation managing vocational training courses that take place in alternation between a training centre and a company.
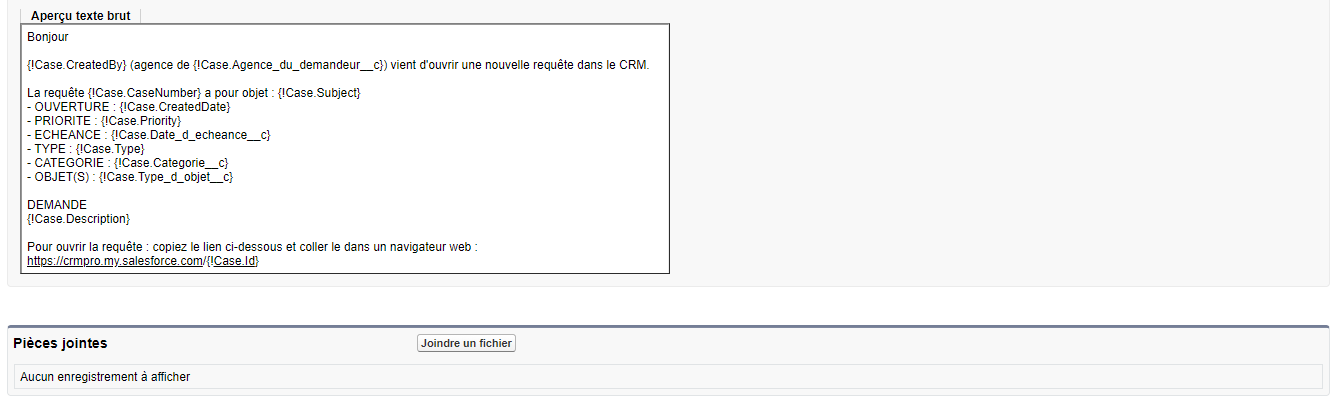
CRM: Customer Relationship Management. A set of technological solutions enabling the strengthening of communication between the company and its customers in order to improve customer relations by automating the various components of the customer relationship (pre-sales - marketing, sales, customer service management, post-sales).
CSS: Cascading Style Sheet. A style sheet that defines the general layout of a website.
DBA: DataBase Administrator. Database Administrator, a professional who manages the availability for users of a database.
DEUST: Diploma of Scientific and Technical University Studies. Professional training (level III - bac +2) prepared in alternating teaching centre / company. The validation of the training offers a French university diploma.
ECM: Enterprise Content Management. Enterprise content management system aimed at managing all the content of an organisation. The aim is to take into account unstructured information in electronic form, such as electronic documents, as opposed to information already structured in databases. The official definition of the term was created by the international organisation AIIM (Association for Information and Image Management) in 2000.
E-LEARNING: In French = e-Formation. E-learning is the use of new multimedia Internet technologies to improve the quality of learning by facilitating access to resources and services on the one hand, and remote exchanges and collaboration on the other. (European Union definition)
E-learning can take place at a distance (online), in the classroom (offline and/or online) or both. E-learning is a specialisation of distance learning, which is a more general concept that includes, among others, correspondence courses, and any other means of teaching in an asynchronous time and place.
ERP: Enterprise Resource Planning. Also called Integrated Management Software (IMP). Applications whose aim is to coordinate all of a company's activities (so-called vertical activities such as production, supply or horizontal activities such as marketing, sales forces, human resources management, etc.) around a single information system.
ERPs generally offer groupware and workflow tools to ensure transversality and the circulation of information between the various departments of the company.
The term "ERP" comes from the name of the MRP (Manufacturing Resource Planning) method used since the 1970s for the management and planning of industrial production.
ESN: Enterprise des Services du Numérique. New name for SSII, a service company with expertise in the field of new technologies and IT. It can encompass several professions (consulting, design and implementation of tools, maintenance or training) and its main objective is to support a client company in the implementation of a project. For more information, see the Wikipedia page.
ETL: Extraction Transfer Loading. Opening connections to various sources, whether applications or production databases.
Objective: to integrate the data required for processing. Schematically, this middleware starts by extracting the content stored by the various business systems before transmitting it to the platform's database.
Until now, ETLs have relied on proprietary connectors to manage the transfers. With the development of Web Services, these interfaces can now make use of a more general-purpose integration technology. Vendors offering this technology include Cognos and Business Objects.
EWB 2001: E-ducation Without Borders - 2001. International conference organised by the students of the Abu Dhabi Men's College from 22 to 24 April 2001 for its first edition. Other editions have been held since then on a biennial basis. The founding theme of these conferences is e-learning (objectives, methods, results). To see the Emirates News Agency article on the first edition, click here "". See e-learning.
FM: Facility Management. Innovative and efficient management method for General and Property Services which consists of bringing together under a single responsibility the management of services to occupants and multi-technical building services. This approach makes it possible to professionalise the service provided, optimise and make costs more flexible, improve the working environment and reduce risks on a professional site.
CMMS: Computerized Maintenance Management System. Software allowing the planning of maintenance operations for a site's equipment with stock management.
CRM: Customer Relationship Management. See CRM.
Groupware. Methods and software (called groupware or synergy software) allowing users to work together in a network.
Thus the term GroupWare refers to various and varied applications with the same goal: to allow geographically distant users to work in teams. Teamwork can take the form of information sharing, or the creation and exchange of computerised data.
KPI: Key Performance Indicators. See KPI.
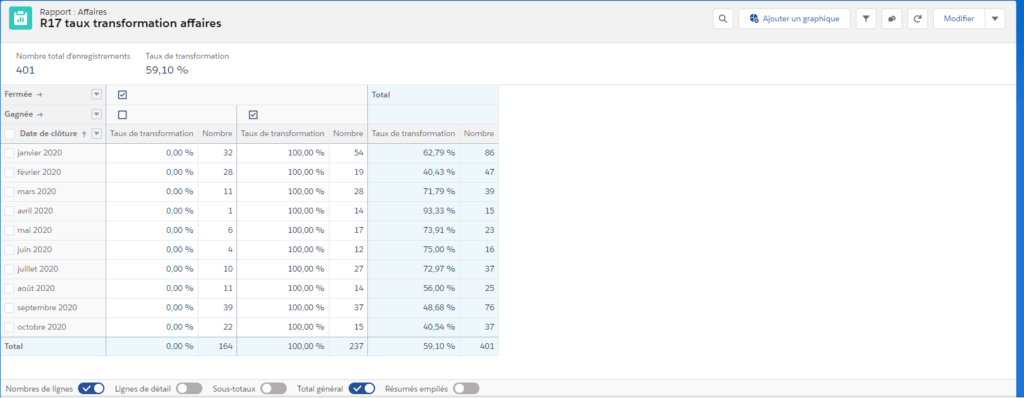
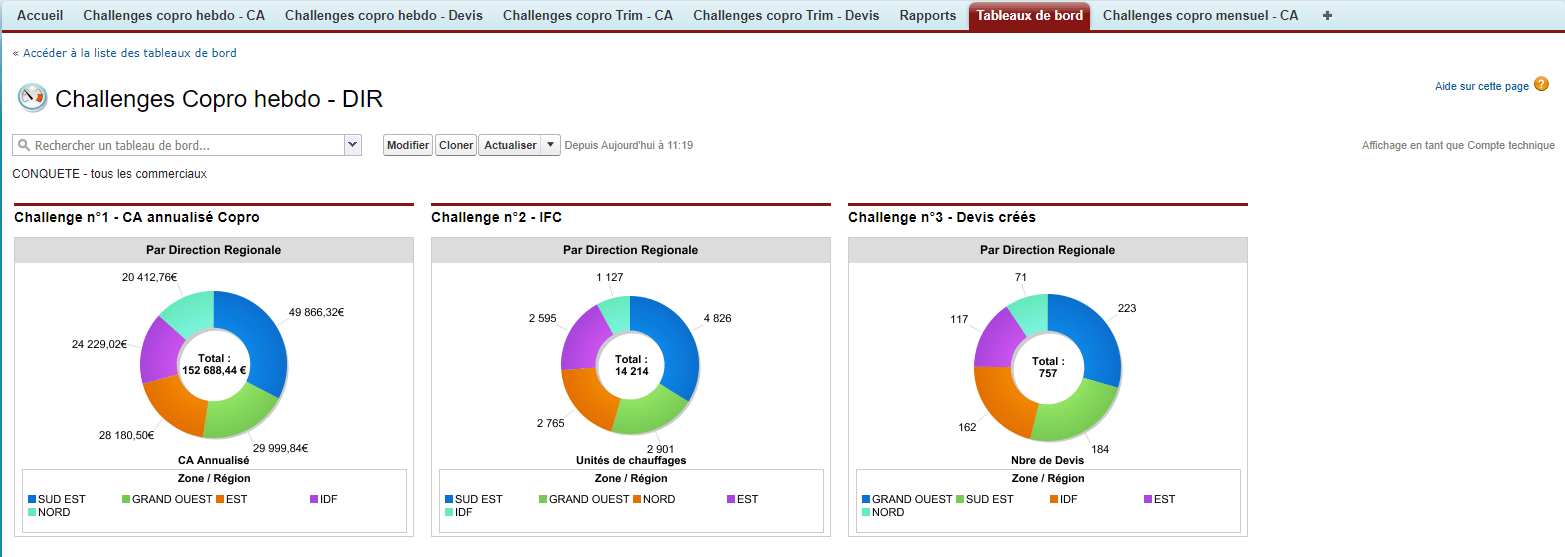
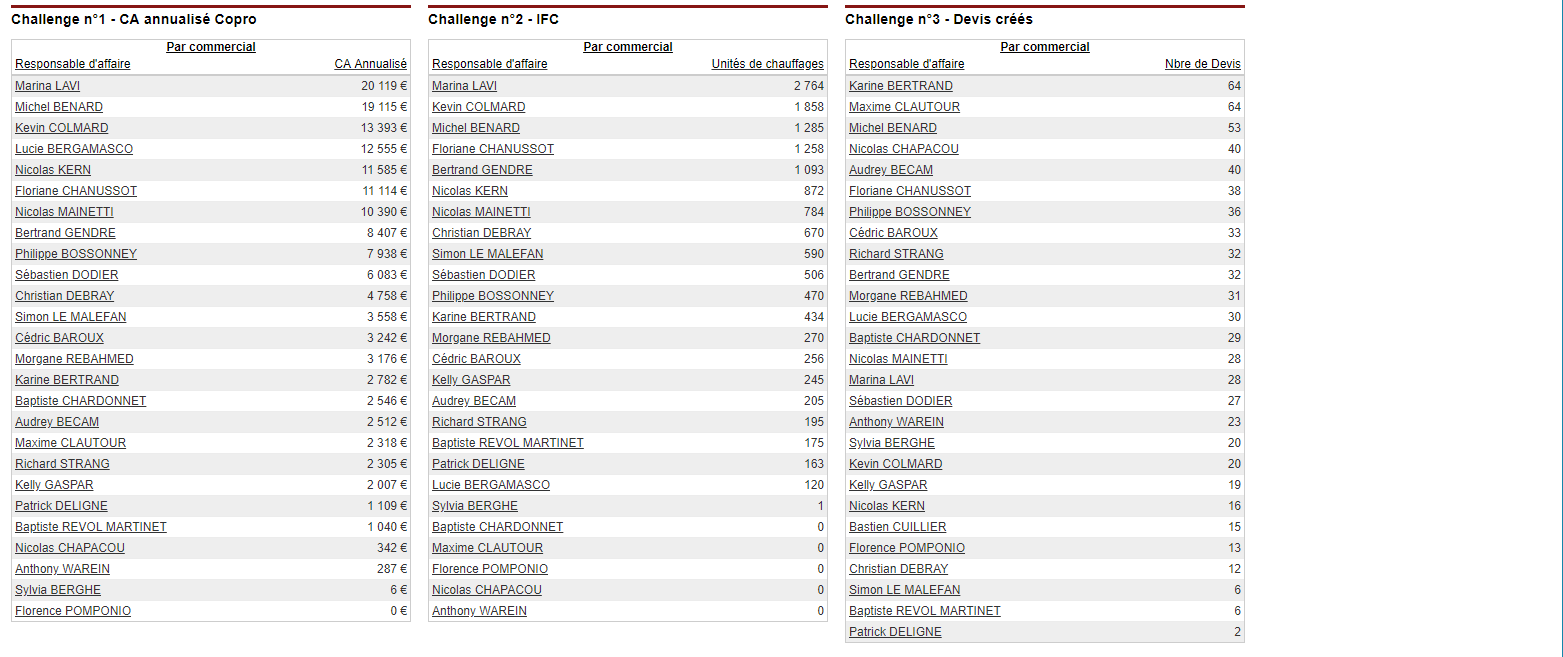
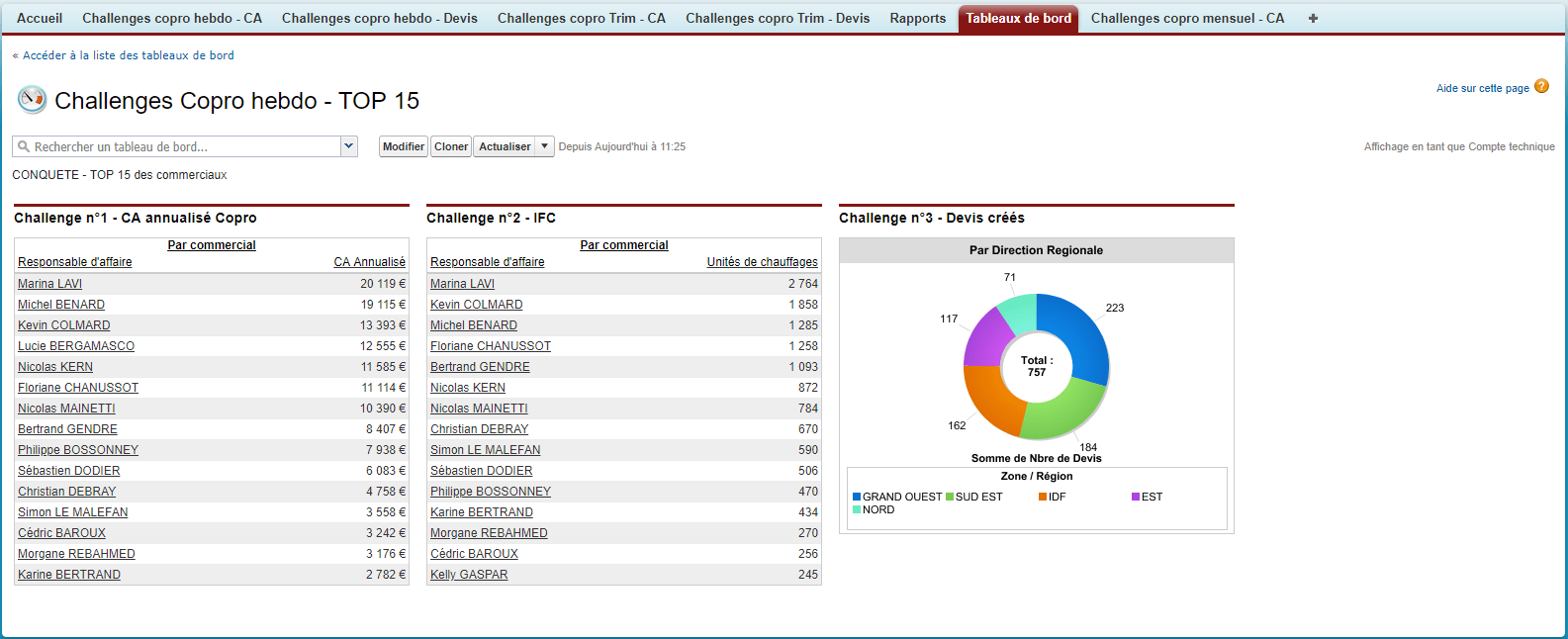
KPI: Key Performance Indicator. Elements for measuring the overall effectiveness of a sales or marketing system or of a particular campaign or action. To ensure the management of an activity, the KPIs can be grouped together in a dashboard.
There are several hundred KPIs that can be used in the context of sales and marketing activities (number of catalogues requested, customer satisfaction, number of orders placed and turnover generated, etc.)
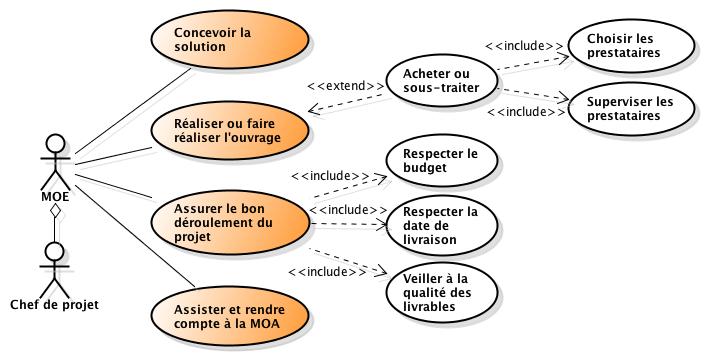
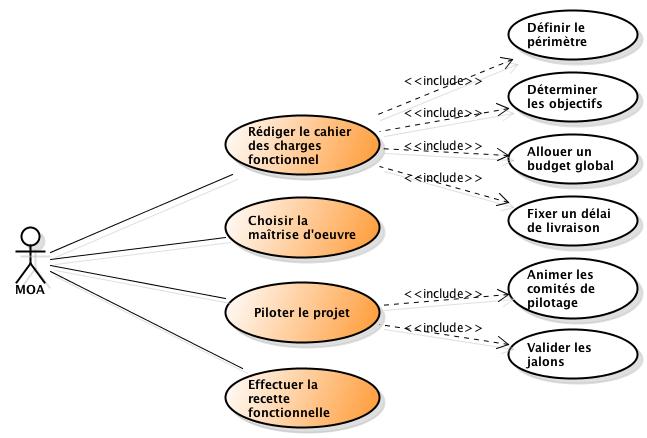
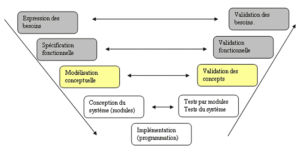
MOA: Project Owner. Representing the client (owner) of the project. The project owner is responsible for managing the project from the reception of user requirements to the testing phase. The different functions of the project owner: Strategic project owner (MOAS), Delegated project owner (MOAD), Operational project owner (MOAO), Project management assistant (AMOA), Business expert. The responsibilities of the Owner. To go further click here "".
MOE: Project Management. It is the guarantor of the good technical realization of the solutions, it provides the product. It can carry out this solution itself, or it can commission one or more suppliers to carry it out. The different functions of the MOE : Design the solution, Carry out the work or have it carried out, Assist and report to the MOA. The responsibilities of the MOE. To go further click here "".
Ohana: Salesforce Ohana. In Hawaiian Ohana means family and family means no one should be abandoned or forgotten. For Salesforce the "Salesforce Ohana" is the family of employees, customers, partners and communities considered "home". They are the heart of everything Salesforce does. Salesforce is grateful for the opportunity to come together as "one" and work to make the world a better place. Salesforce's Ohana is based on four core values: Trust, Growth, Innovation and Equality.
ERP: Integrated Management Software. See ERP.
Portfolio: Personal file. A personal file that references a person's learning and experience. The aim is to obtain recognition by an educational institution or an employer by demonstrating one's skills. With the development of new technologies, it is now referred to as a digital portfolio or cyberfolio.
The portfolio differs from the CV in that the information it contains is articulated with a purpose, such as a job application, and it must also present evidence of the individual's achievements.
PO: Product Owner. Person in charge of carrying out a project following the Agile methodology. He/she combines technical know-how in the design and definition of the product's characteristics in order to provide maximum business value to users (within the time and budget allocated to the project), with professional knowledge in the management of the implementation teams and in exchanges with clients.
PM: Property Management. Property Management is the legal and administrative management of real estate on behalf of an owner. Property management includes, among other things, the management of leases, rental, maintenance of the building, etc.
RAID: Redundant Array of Inexpensive Disks or Redundant Array of Independent Disks. A technology that allows the creation of a storage unit from several hard disks. The unit thus created (called a cluster) has a high fault tolerance (high availability), or a higher capacity/writing speed. The distribution of data over several hard disks increases security and reliability of the associated services.
Disks assembled using RAID technology can be used in different ways, known as RAID levels. The University of California has defined 5 RAID levels, each of which describes the way in which data is distributed across the drives:
- Level 0: called striping
- Level 1: called mirroring, shadowing or duplexing
- Level 2: called striping with parity (obsolete)
- Level 3: called disk array with bit-interleaved data
- Level 4: called disk array with block-interleaved data
- Level 5: called disk array with block-interleaved distributed parity
RMAN: Recovery MANager. Tool for managing backups and restorations of an oracle database. Product provided by ORACLE.
SCRUM: Scrum scheme. A complex product development organization scheme defined as a "holistic iterative framework that focuses on common goals by productively and creatively delivering products of the highest possible value".
DBMS: Database Management System. A collection of software that allows the creation, management and interrogation of a database, regardless of the application domain.
SQL: Structured Query Language. A comprehensive query management language for DBMSs based on relational algebra. SQL is used for defining, inserting, updating and querying data and data types.
SSII: Société de Service en Ingénierie Informatique. See ESN.
TCP/IP: Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol. The TCP/IP protocol represents the way computers communicate on the Internet.
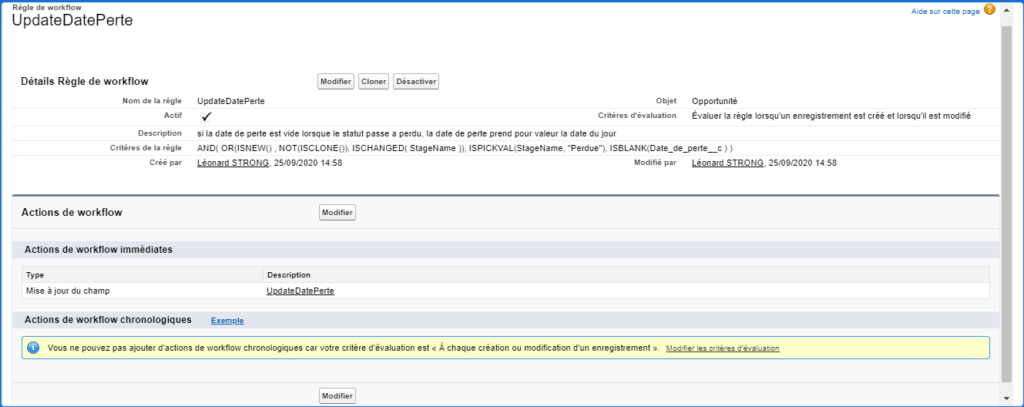
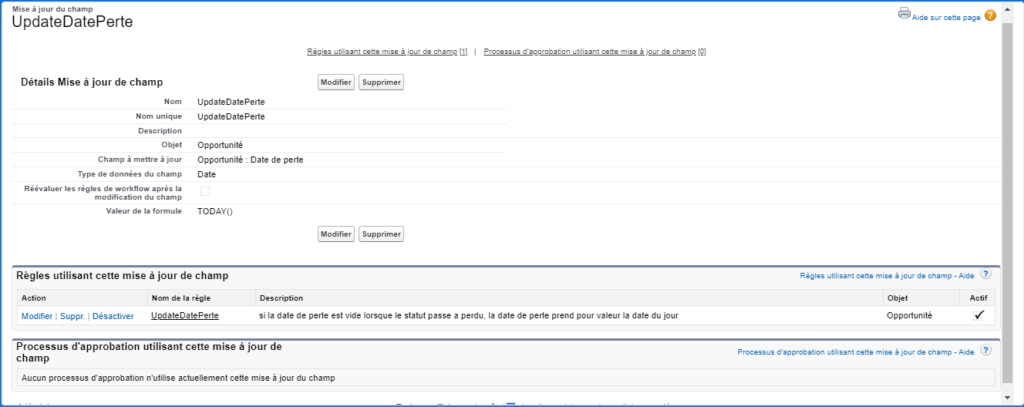
WorkFlow: Electronic business process management. Modelling and management of all the tasks to be carried out and the different actors involved in the realisation of a business process (also called operational process).
There are generally two types of workflows:
- Procedural workflow (also called production workflow or directive workflow) corresponding to business processes known to the company and subject to pre-established procedures: the workflow path is more or less fixed;
- The ad hoc workflow based on a collaborative model in which the actors intervene in the decision of the path: the workflow path is dynamic.
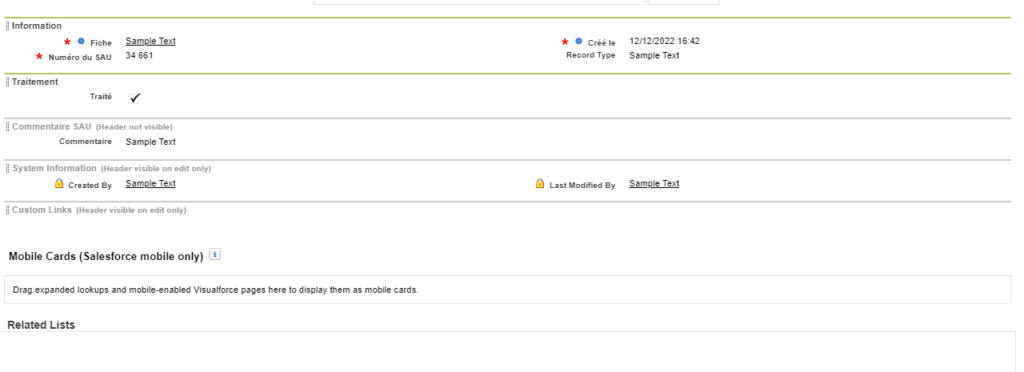
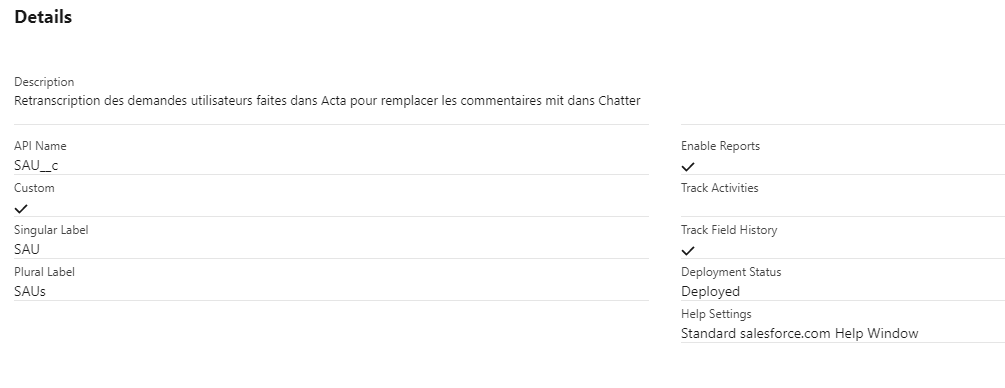
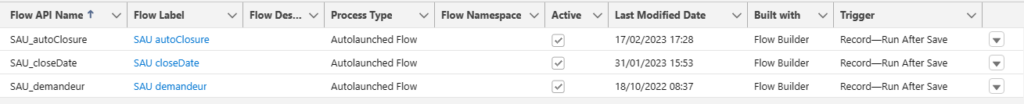
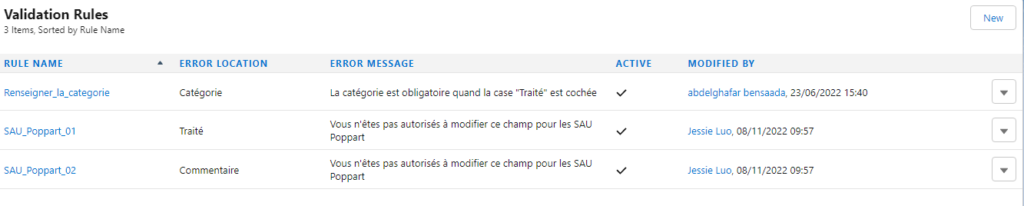
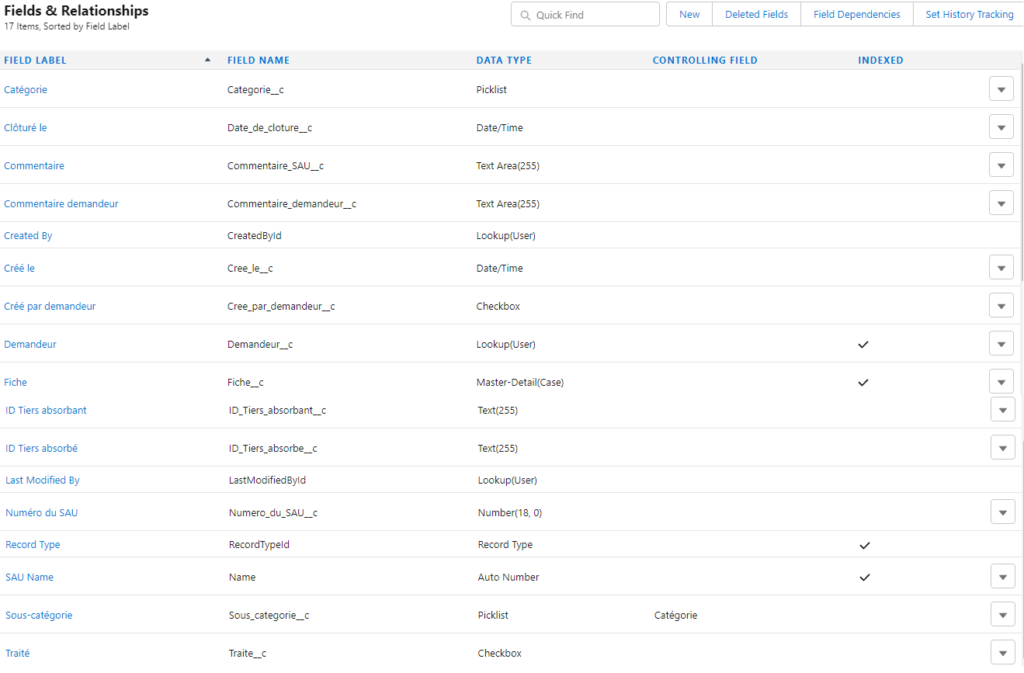
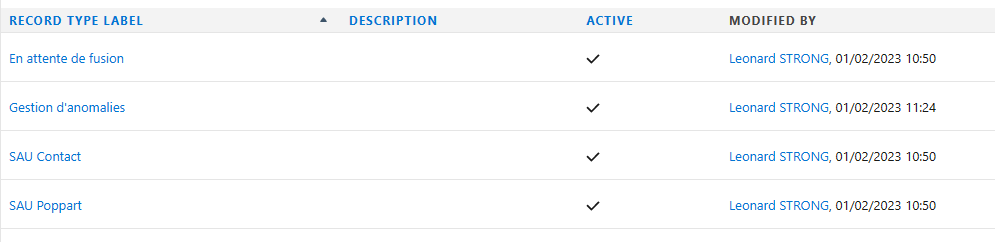
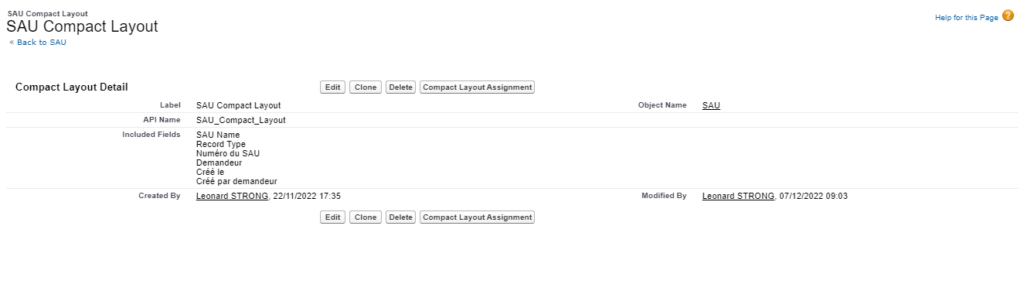
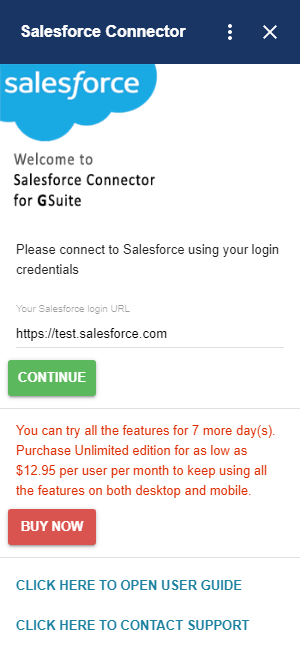
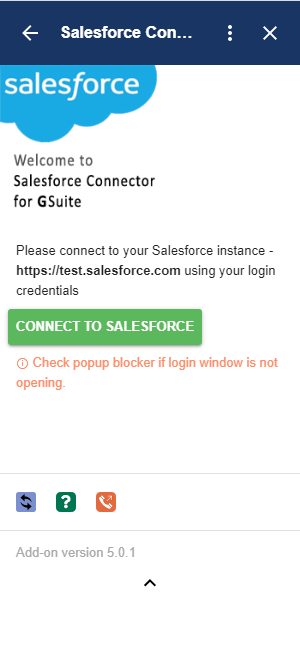
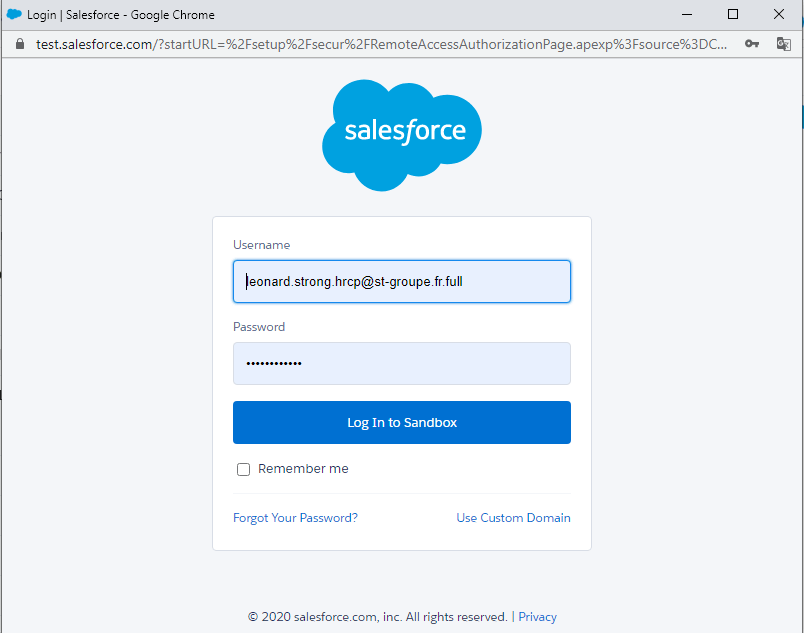

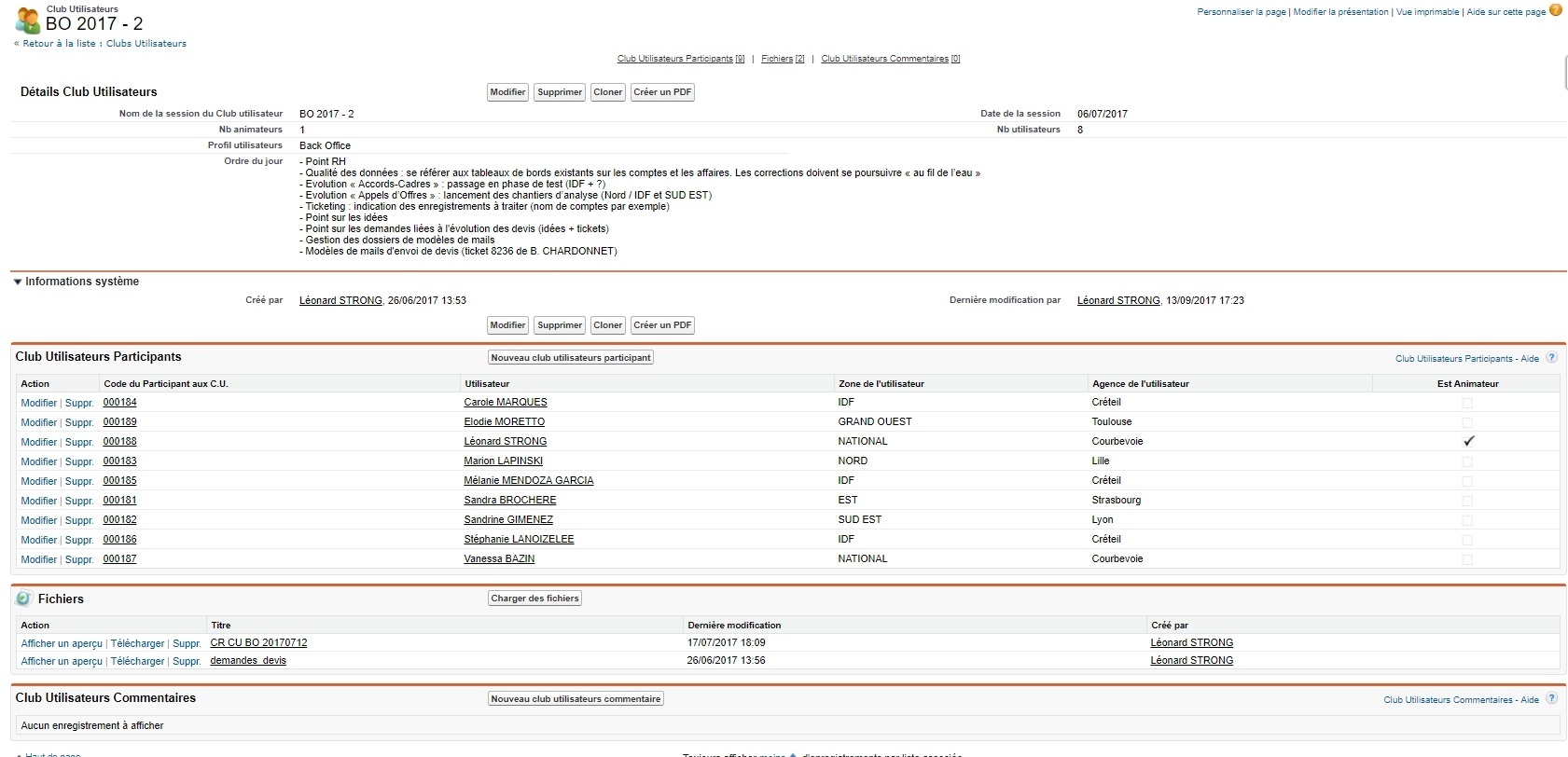

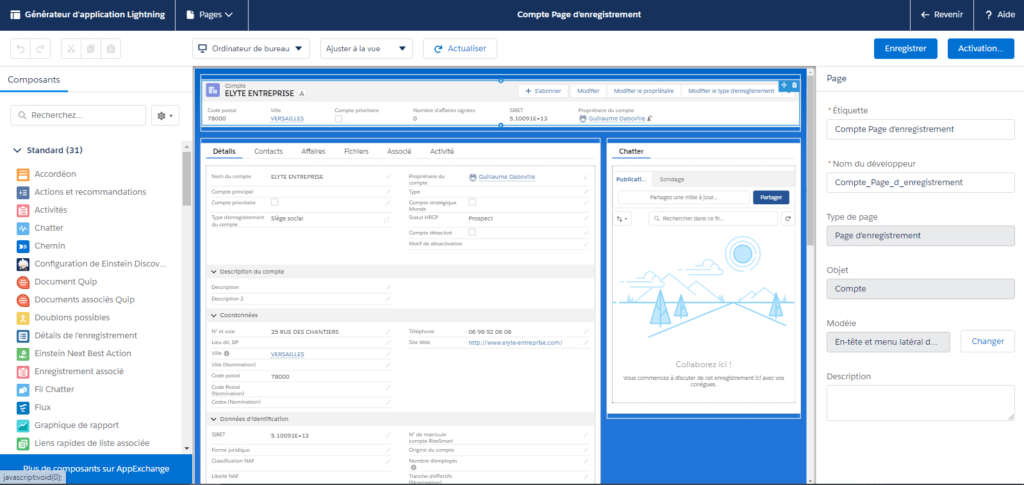
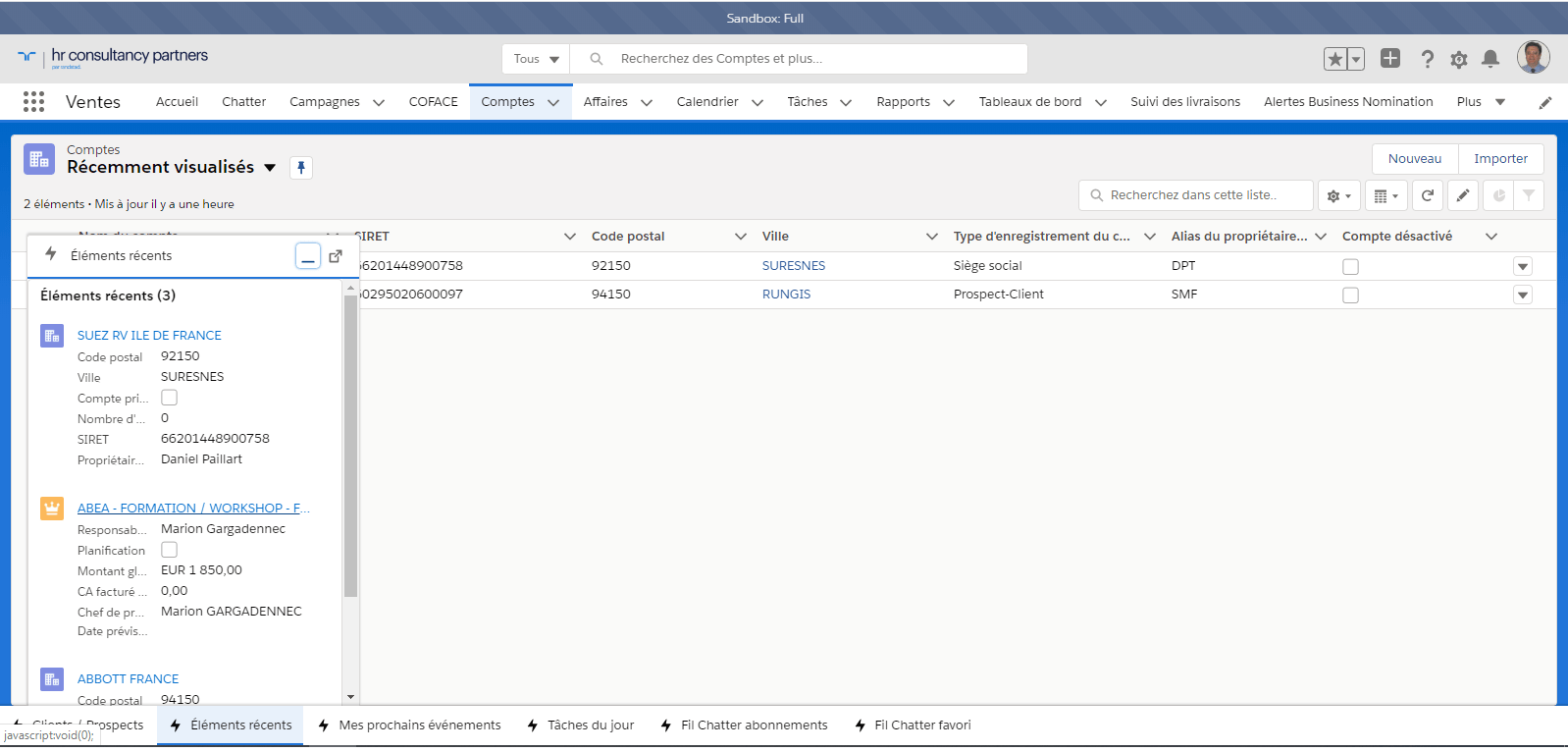
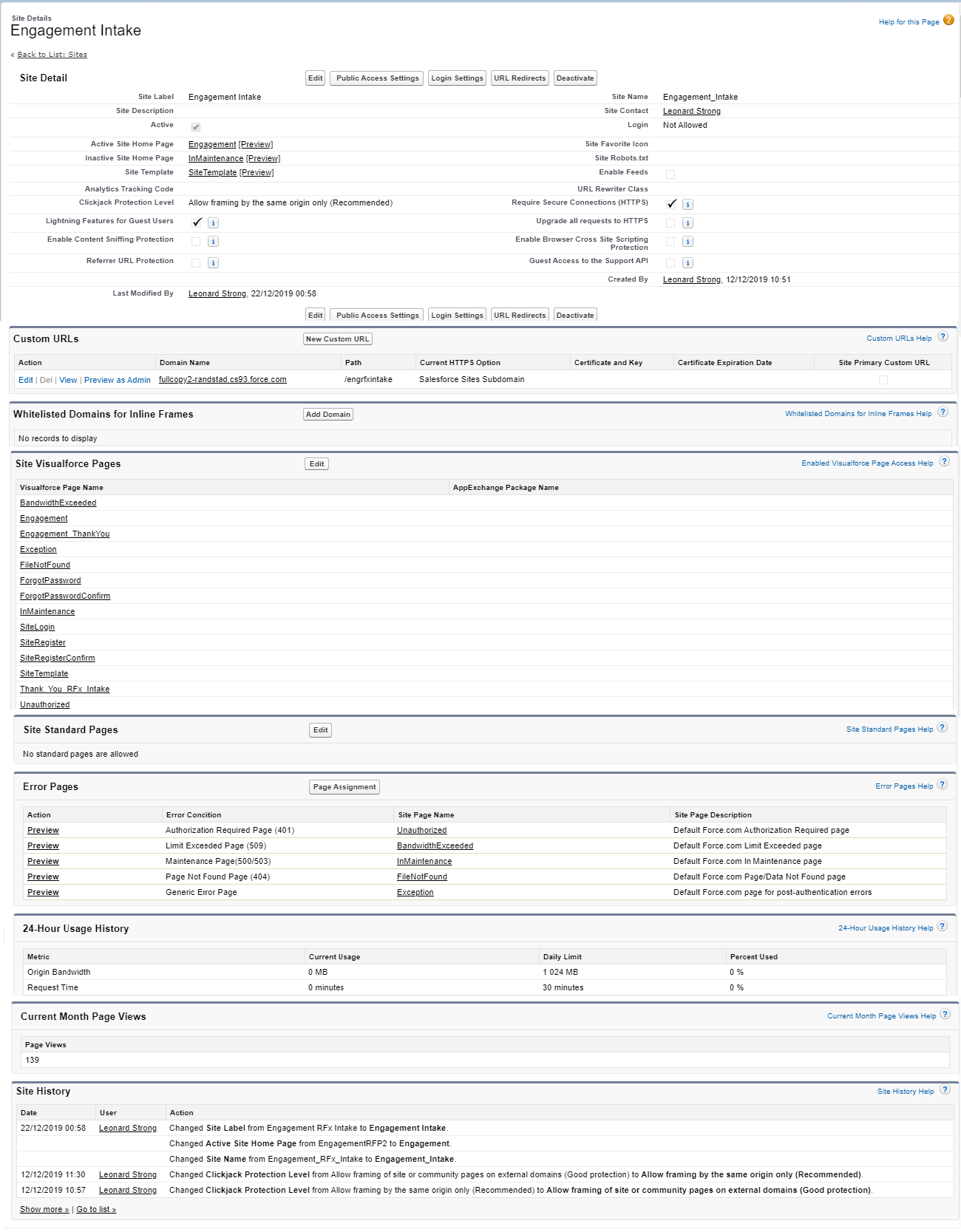
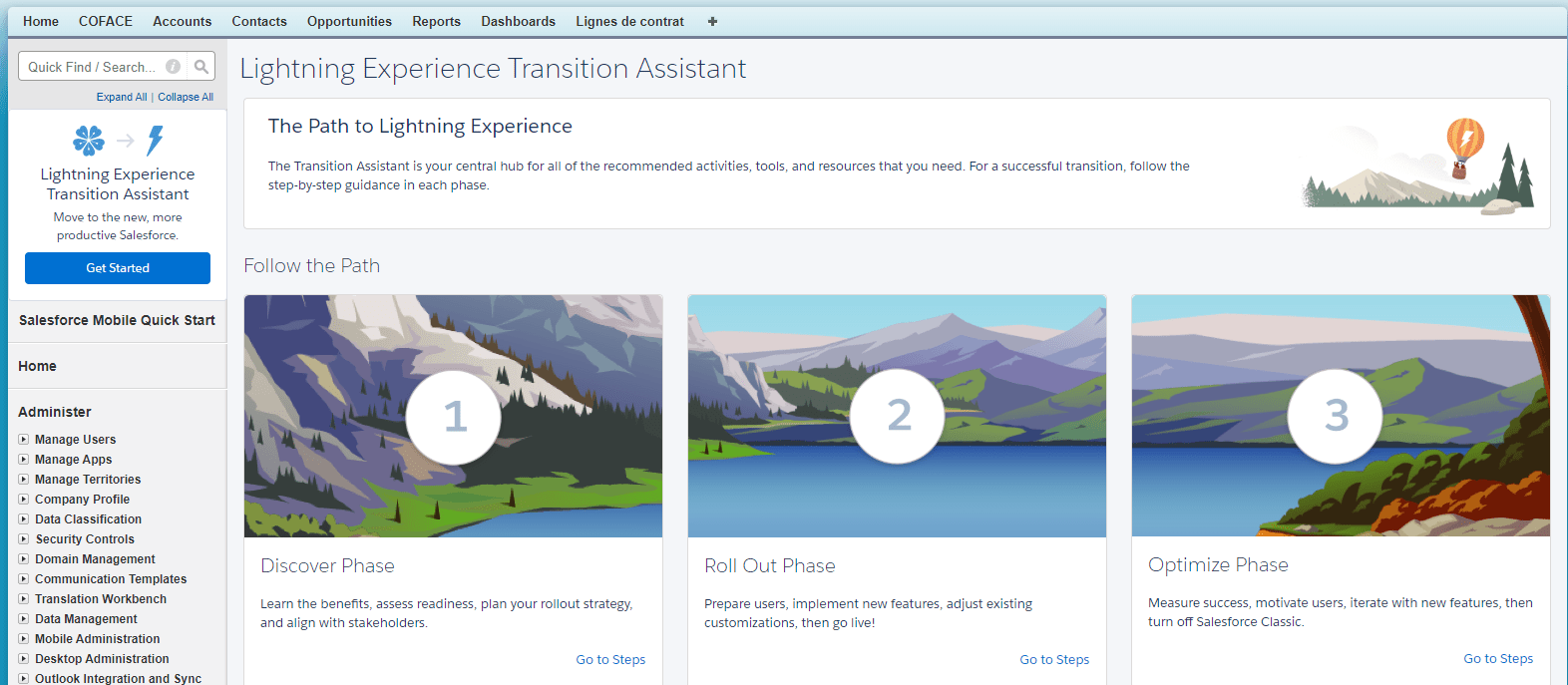
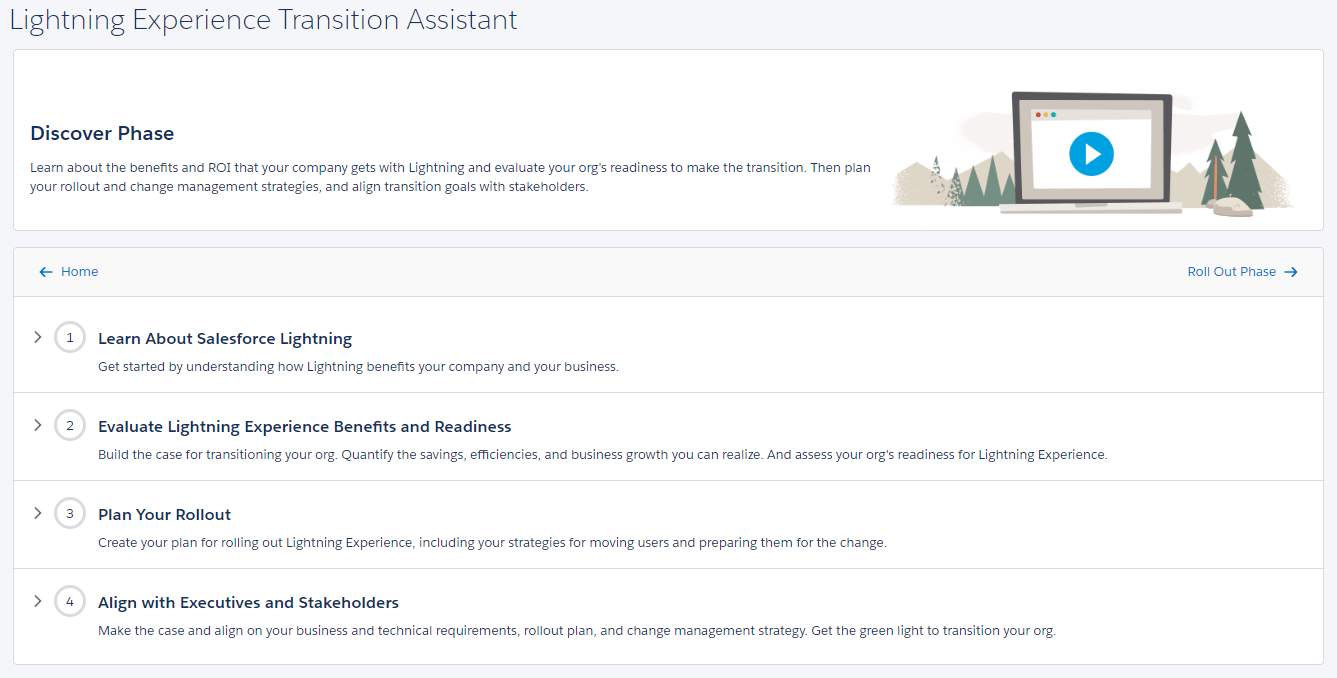
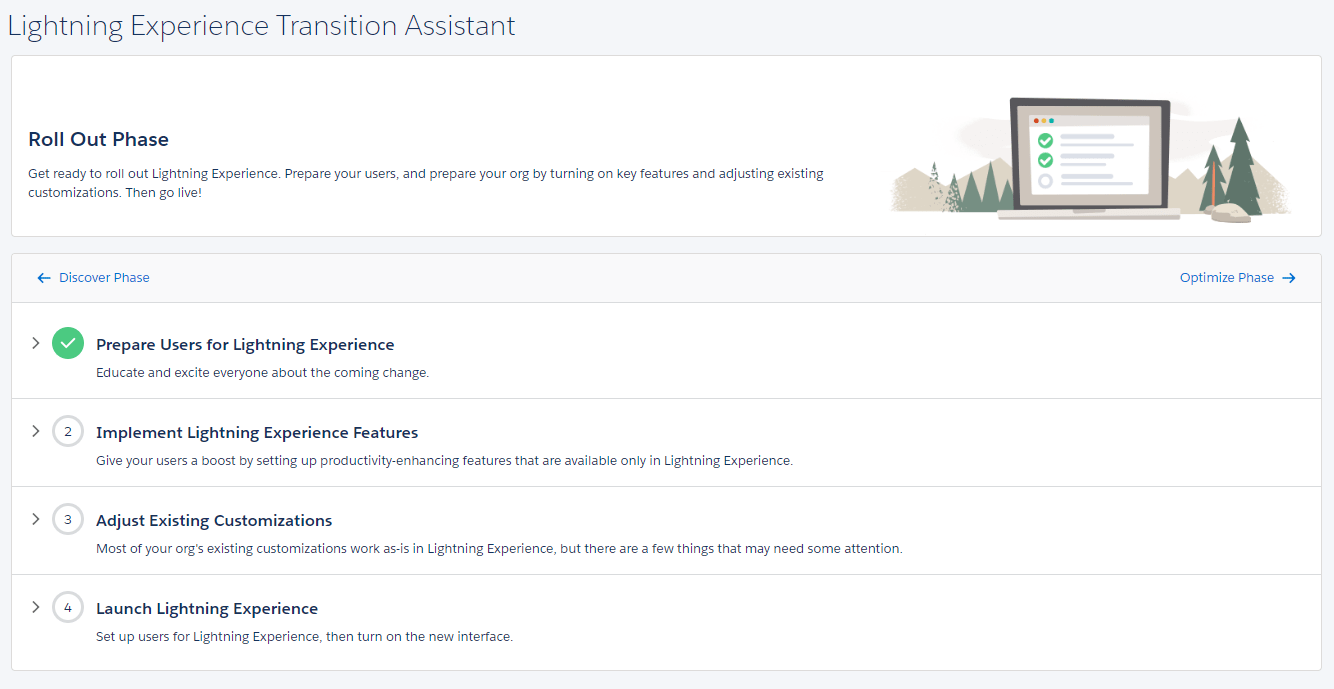
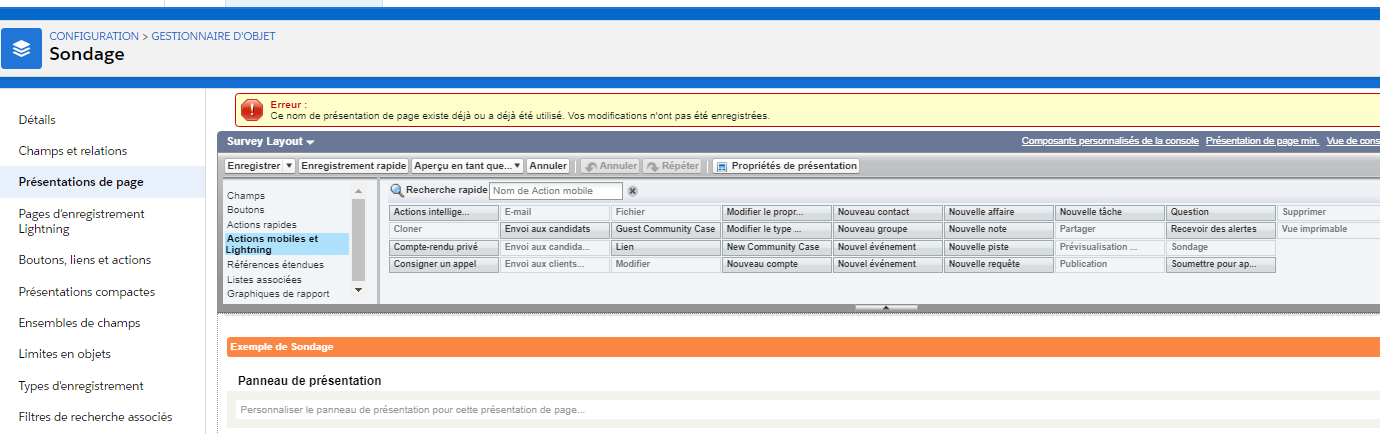 Under Lightning the resolution procedure is described on this
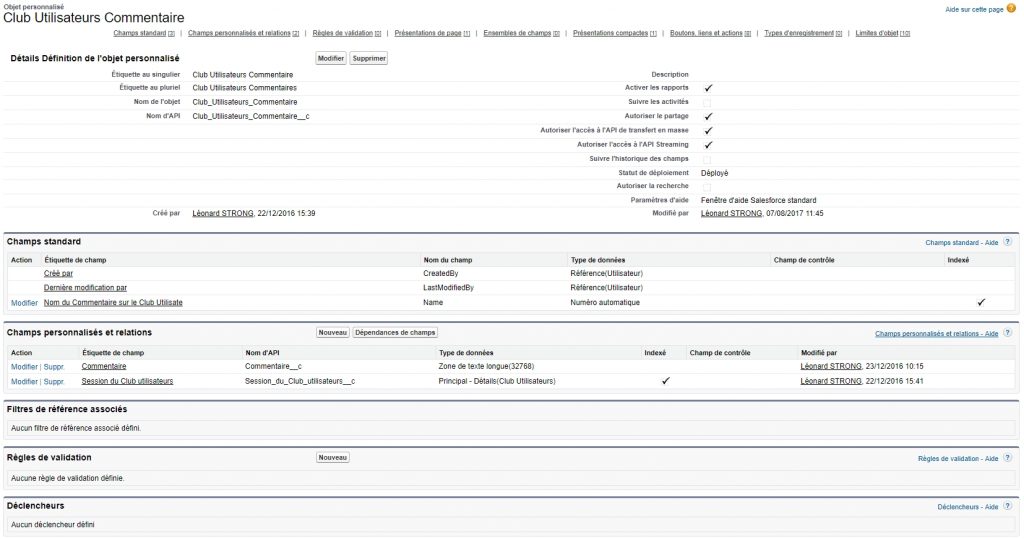
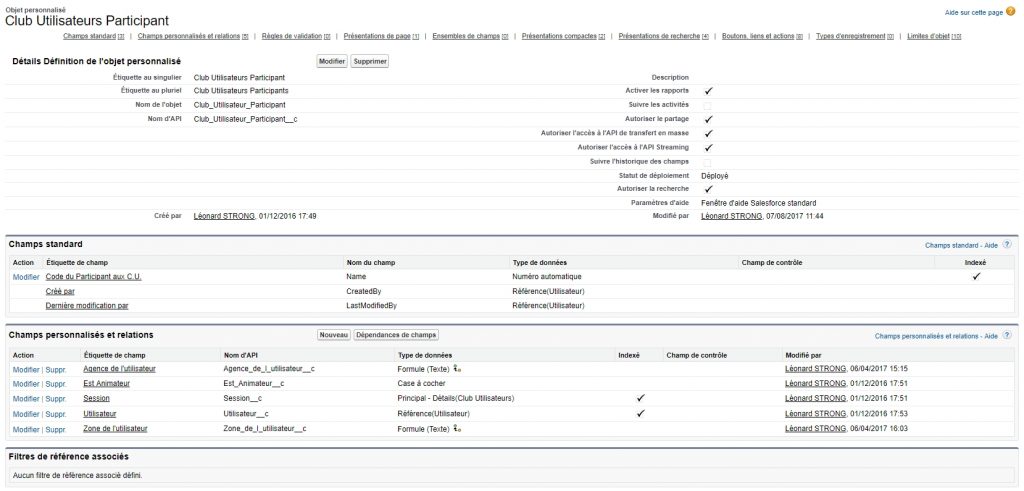
Under Lightning the resolution procedure is described on this